Description:
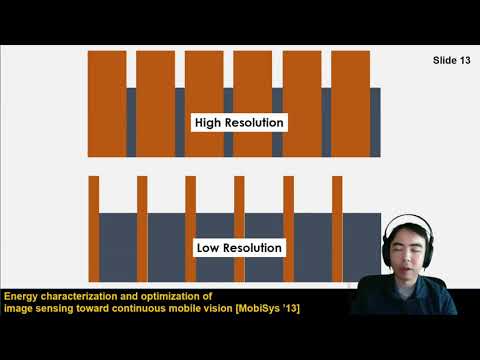
Explore system support for efficient multi-resolution visual computing on mobile devices in this tinyML Talks webcast. Delve into challenges and opportunities for mobile operating systems and vision sensing pipeline architectures to flexibly support dynamic multi-resolution workloads. Learn about energy-saving techniques, including sacrificing image resolution when high detail is unnecessary for computer vision and augmented reality tasks. Discover the Banner media framework for seamless resolution reconfiguration and ongoing efforts in multi-resolution visual computing systems. Gain insights into driver-based power optimization, energy-proportionality, and format-oblivious memory management. Understand the importance of rapid reconfigurability at low latencies and expressiveness to meet computational needs with minimal developer burden in mobile systems.
System Support for Efficient Multi-Resolution Visual Computing on Mobile Systems
Add to list