Description:
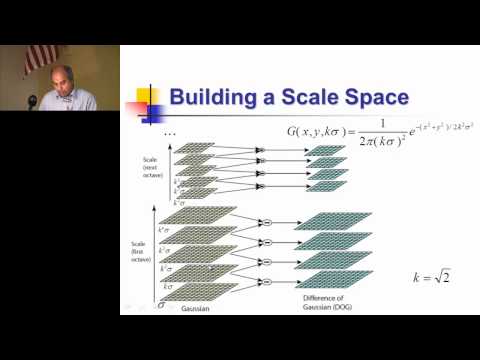
Explore the Scale-invariant Feature Transform (SIFT) in this comprehensive lecture from the UCF Computer Vision Video Lectures 2012 series. Delve into the intricacies of SIFT, developed by David Lowe at UBC, as Dr. Mubarak Shah guides you through key point extraction, advantages, and invariant local features. Learn the steps for extracting key points, including scale space concepts, approximation of LOG by Difference of Gaussians, and building a scale space. Discover techniques for scale space peak detection, key point localization, and outlier rejection. Examine orientation assignment and its similarity to the IT cortex. Master the extraction of local image descriptors at key points, understanding descriptor regions and key point matching. Gain valuable insights into this powerful computer vision technique through detailed explanations and visual aids.
Scale-invariant Feature Transform (SIFT) - Lecture 5
Add to list
#Computer Science
#Artificial Intelligence
#Computer Vision
#Machine Learning
#Feature Extraction
#Pattern Recognition