Description:
Explore digital logic concepts in this comprehensive lecture covering JK flip-flops, state transition tables, flip-flop conversions, registers, serial interfaces, counters, and finite state machines. Delve into topics such as serial-to-parallel shift registers, SPI and USB protocols, synchronous and asynchronous counter designs, and the differences between Moore and Mealy machines. Learn how to create state transition diagrams, implement Gray coding, and understand the practical applications of these digital logic components in electronic systems.
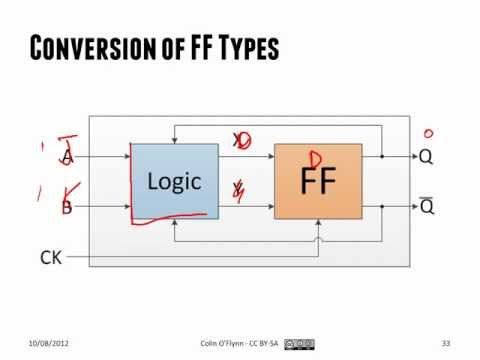
Course Review Lecture Part 3 - Aug 10, 2012
Add to list
#Computer Science
#Automata Theory
#Finite State Machine
#Engineering
#Electrical Engineering
#Circuit Design