Description:
Explore cell migration mechanisms in a 37-minute webinar featuring Dr. Kristin Bircsak's presentation on 3D cell migration using a microfluidic endothelium-on-a-chip model. Delve into the essential process of cell migration and its role in wound healing, cancer metastasis, and immune system function. Learn about the OrganoPlate technology and its applications in studying immune cell extravasation and infiltration. Discover how to visualize and quantify T cell migration, generate chemokine gradients, and induce vascular inflammation in microfluidic chips. Gain insights into donor-to-donor differences, blocking T cell extravasation, and the compatibility of immune migration assays with various cell types. Understand the potential of human tissue models for developing better therapies and advancing our understanding of complex biological phenomena.
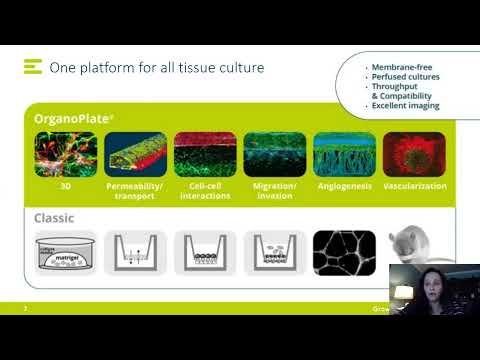
3D Cell Migration Using a Microfluidic Endothelium-on-a-Chip Model
Add to list
#Science
#Biology
#Cell Biology
#Cell Migration
#Immune System
#Physics
#Fluid Mechanics
#Fluid Dynamics
#Microfluidics