Description:
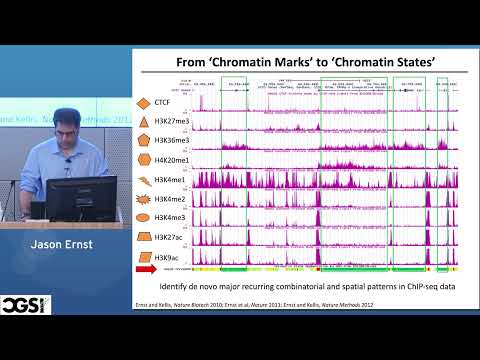
Explore computational methods for modeling and analyzing epigenomic data in this 45-minute tutorial from the Computational Genomics Summer Institute. Delve into supervised integration of multiple chromatin markers using multivariate Hidden Markov Models, specifically focusing on the ChromHMM approach. Examine the ENCODE project's study of nine marks in nine human cell lines and discover how chromatin state annotations reveal cell type-specific enrichments of GWAS hits. Learn about regulatory activity in DNA accessible sites and its dependence on chromatin state. Compare three options for applying ChromHMM to multiple cell types, including the advantages of stacked modeling over concatenated models. Investigate the application of ChromGene to Roadmap Epigenomics data and its relationship with gene expression. Gain insights from related research papers on genome annotation, human-mouse conservation scoring, and large-scale imputation of epigenomic datasets for systematic tissue annotation.
Read more
A Tutorial on Computational Methods for Modeling and Analyzing Epigenomic Data
Add to list
#Science
#Biology
#Epigenetics
#Epigenomics
#Computer Science
#Machine Learning
#Hidden Markov Models
#Data Science
#Bioinformatics
#Computational Biology
#Genomics
#Genome Annotation
0:00 / 0:00