Description:
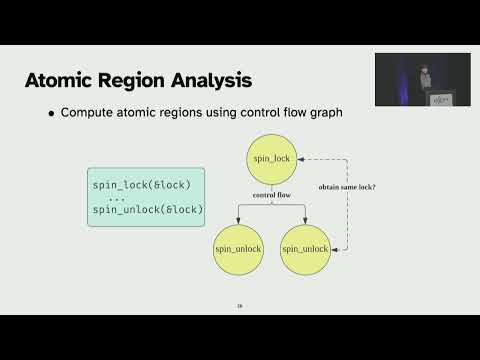
Explore an innovative framework for automating device driver isolation in modern kernels through this OSDI '22 conference talk. Dive into the challenges of isolating device drivers and learn how KSplit addresses them by performing automated analyses on unmodified kernel and driver source code. Discover how KSplit identifies shared state between the kernel and driver, computes synchronization requirements for efficient isolation, and handles ambiguous pointers. Examine the evaluation of KSplit on nine Linux kernel subsystems, covering 354 device drivers, with a focus on the complex Ixgbe driver. Gain insights into the practical application of KSplit, including the minimal manual changes required and its potential for automating key tasks in driver isolation. Understand the performance implications and the broader impact of this approach on kernel security and reliability.
KSplit - Automating Device Driver Isolation
Add to list
0:00 / 0:00